Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Kurikami, Hiroshi; Niizato, Tadafumi; Tsuruta, Tadahiko; Kato, Tomoko; Kitamura, Akihiro; Kanno, Mitsuhiro*; Kurosawa, Naohiro*
JAEA-Research 2016-020, 50 Pages, 2017/01
In this report, we developed a compartment model of radionuclide migration in environment based on exposure pathways in a river basin scale and performed a preliminary calculation. The results showed good agreement with some measurement, although the comparison of bed sediment, transportation to outer sea and to agricultural products with the measurement was not enough. We continue to validate the model.
Yang Zumao*;
JNC TN9400 2000-009, 81 Pages, 2000/02
It is important to study thermal stratification and striping phenomena for they can induce thermal fatigue failure of structures. This presentation uses the AQUA code, which has been developed in Japan Nuclear Cycle Development Institute (JNC), to investigate the characteristics of these thermal phenomena in water, liquid sodium, liquid lead and carbon dioxide gas. There are altogether eight calculated cases with same Richardson number and initial inlet hot velocity in thermal stratification calculations, in which four cases have same velocity difference between inlet hot and cold fluid, the other four cases with same temperature difference. The calculated results show : (1) The fluid's properties and initial conditions have considerable effects on thermal stratification, which is decided by the combination of such as thermal conduction, viscous dissipation and buoyant force, etc., and (2) The gas has distinctive thermal stratification characteristics from those of liquid because for
JNC TN9400 2000-008, 323 Pages, 2000/02
This rport presents numerical results on theemal striping characteristics at a tee junction of LMFBR coolant pipe, carried out using a direct numerical simulation code DINUS-3. In the numerical investigations, it was considered a tee junction system consisted of a main pipe (1.33 cm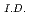 ) with a 90
) with a 90 elbow and a branch pipe, and four parameters, j.e., (1)diameter ratio
elbow and a branch pipe, and four parameters, j.e., (1)diameter ratio  between both the pipes, (2)flow velocity ratio
between both the pipes, (2)flow velocity ratio  between both the pipes, (3)angle
between both the pipes, (3)angle  between both the pipes, and (4)Reynolds number Re. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)According to the decreasing of the diameter ratio, significant area of second-order moments was expanded in the fixed condition of
between both the pipes, and (4)Reynolds number Re. From the numerical investigations, the following characteristics were obtained: (1)According to the decreasing of the diameter ratio, significant area of second-order moments was expanded in the fixed condition of  =1.0. (2)Significant second-order moments area was expanded for the increasing of the flow velocity ratio
=1.0. (2)Significant second-order moments area was expanded for the increasing of the flow velocity ratio  specified by varying of the main pipe velocity in the case of a
specified by varying of the main pipe velocity in the case of a  = 1.0 constant condition. 0n the other hand, the area was expanded for the decreasing of the velocity ratio
= 1.0 constant condition. 0n the other hand, the area was expanded for the decreasing of the velocity ratio  defined by varying of the branch pipe velocity in the case of a
defined by varying of the branch pipe velocity in the case of a  = 3.0 constant condition. (3)Maximum second-order moments values were generated in the case of
= 3.0 constant condition. (3)Maximum second-order moments values were generated in the case of  = 180
= 180 due to the influence of interactions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe. (4)According to the increase of Reynolds number, significant area of second-order moments was expanded due to the activation of turbulence mixing in the main pipe.
due to the influence of interactions between main pipe flows and jet flows from the branch pipe. (4)According to the increase of Reynolds number, significant area of second-order moments was expanded due to the activation of turbulence mixing in the main pipe.
; ; Kamide, Hideki
JNC TN9400 2000-026, 70 Pages, 1999/11
The phenomena on a thermal-hydraulic field inside/outside the porous blockage has been investigated by the experiment employed the 4-subchamlel geometry water test facility. From existing experimental and numerical studies, it was shown that the now field around the blockage had significant effect on the temperature distribution inside the blockage. Therefore, We conducted the experiment of flow visualization with 4-subchannel geometry water test facility. The flow visualization showed that the recirculation flow and a lateral flow existed at the side of the porous blockage. The region of recirculation flow extended to the downstream side with increasing of the flow rate. The mixing due to the convection was dominant in the region of recirculation flow, and was getting effective as increasing of the flow rate. ln the wake region, the flow was unstable due to the interaction between the flows in the unplugged and plugged subchannels. The coolant was provided from the unplugged subchannels and also through the inside of porous blockage. These results obtained from the flow visualization gathering with the numerical simulation will be reflect to the evaluation of the local blockage issue of large scale Fast Breeder Reactor.
Matsunaga, Takeshi
JAERI-Conf 99-001, p.258 - 269, 1999/03
no abstracts in English
M.S.Islam*; Hino, Ryutaro; Haga, Katsuhiro; Monde, Masanori*; Sudo, Yukio
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 35(9), p.671 - 678, 1998/09
Times Cited Count:17 Percentile:77.73(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Takase, Kazuyuki; Hino, Ryutaro;
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi, 33(10), p.975 - 982, 1991/10
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:19.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
 Cs in the Kuji River, Japan
Cs in the Kuji River, JapanMatsunaga, Takeshi; Amano, Hikaru; Yanase, Nobuyuki
Applied Geochemistry, 6(2), p.159 - 167, 1991/00
Times Cited Count:36 Percentile:65.63(Geochemistry & Geophysics)no abstracts in English
Kurikami, Hiroshi; Malins, A.; Kitamura, Akihiro; Mori, Koji*; Tada, Kazuhiro*; Kobayashi, Takamaru*
no journal, ,
We added models of erosion, transport and deposition of sediment due to surface flow and corresponding radioactive cesium transport into GETFLOWS, GEneral purpose Terrestrial fluid-FLOW Simulator. The application of the model showed results in good agreement with the monitored turbidity and radioactive cesium concentrations in rivers.
Taniguchi, Keisuke*; Takeuchi, Yukio*; Fujita, Kazuki*; Dohi, Terumi; Hayashi, Seiji*; Kuramoto, Takayuki*; Nomura, Naoki*; Aono, Tatsuo*
no journal, ,
In Fukushima Prefecture, although decontamination has been completed except for difficult-to-return areas, most of the forest has not been decontaminated yet. From the forest, radiocaesium may enter rivers and affect downstream areas. A survey was conducted in three forested watersheds of the Nanokazawa, Saruta, Nuno rivers located in Fukushima Prefecture to understand the amount and characteristics of radiocaesium flowing out. In each watershed, suspended solids (SS) were collected by a suspended sand sampler, water was collected every few months, and the water level and flow rate were measured. After freeze-drying the SS sample, the concentration of suspended Cs-137 was measured by a germanium semiconductor detector. The water sample was filtered through a membrane filter with a pore size of 0.45  m, then the dissolved Cs-137 was collected by the solid-phase extraction disk method or AMP coprecipitation method, and the dissolved Cs-137 concentration was measured by a germanium semiconductor detector. The ranges of dissolved Cs-137 concentration in FY2019 were 69-190 mBq/L in the Saruta River, 9.7-16 mBq/L in the Nanokazawa river, and ND-3.2 mBq/L in the Nuno River. In the poster, we will also present the results of SS measurements and flow observations.
m, then the dissolved Cs-137 was collected by the solid-phase extraction disk method or AMP coprecipitation method, and the dissolved Cs-137 concentration was measured by a germanium semiconductor detector. The ranges of dissolved Cs-137 concentration in FY2019 were 69-190 mBq/L in the Saruta River, 9.7-16 mBq/L in the Nanokazawa river, and ND-3.2 mBq/L in the Nuno River. In the poster, we will also present the results of SS measurements and flow observations.
Aono, Tatsuo*; Nakanishi, Takahiro
no journal, ,
In order to elucidate the distribution, behavior and runoff process of radiocaesium in stream water collected from forest catchments, the activity concentrations of dissolved and particulate radiocaesium were monitored in this area. Although there is a very strong correlation between annual mean activity concentration of dissolved Cs-137 and mean air does rate in catchment area, no features were found with activity concentrations of particulate Cs-137 and mean air does rate in the area. The river water increased due to heavy rains caused by two typhoons in October 2019, and then the topography changed drastically with the inflow of sediment. The radioactivity concentrations of dissolved Cs-137 were decreased by about 50% compared to before the heavy rain. However, the change of radioactivity concentrations of particulate Cs-137 have not been observed. It is considered that the condition of the forest basin has changed as one of reasons.
Ikenoue, Tsubasa; Shimadera, Hikari*; Kondo, Akira*
no journal, ,
We evaluated the environmental fate of  Cs in the Abukuma River Basin from 2011 to 2040 by using a distributed radiocesium prediction model. The model well reproduced interannual variations in the concentration of
Cs in the Abukuma River Basin from 2011 to 2040 by using a distributed radiocesium prediction model. The model well reproduced interannual variations in the concentration of  Cs in the suspended sediment and the total outflow of
Cs in the suspended sediment and the total outflow of  Cs at Iwanuma near the estuary. Thirty years after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, it was estimated that the concentration of
Cs at Iwanuma near the estuary. Thirty years after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident, it was estimated that the concentration of  Cs in the suspended sediment decreased to 1.9% of the concentration in the earliest phase after the accident and the total outflow of
Cs in the suspended sediment decreased to 1.9% of the concentration in the earliest phase after the accident and the total outflow of  Cs was equivalent to 4.6% of the initial deposition in the Abukuma River basin.
Cs was equivalent to 4.6% of the initial deposition in the Abukuma River basin.